Lecture 2: Introducing Python¶
CSCI 1360E: Foundations for Informatics and Analytics
Overview and Objectives¶
In this lecture, I'll introduce the Python programming language and how to interact with it; aka, the proverbial Hello, World! lecture. By the end, you should be able to:
- Recall basic history and facts about Python (relevance in scientific computing, comparison to other languages)
- Print arbitrary strings in a Python environment
- Create and execute basic arithmetic operations
- Understand and be able to use variable assignment and update
Part 1: Background¶
Python as a language was implemented from the start by Guido van Rossum. What was originally something of a snarkily-named hobby project to pass the holidays turned into a huge open source phenomenon used by millions.
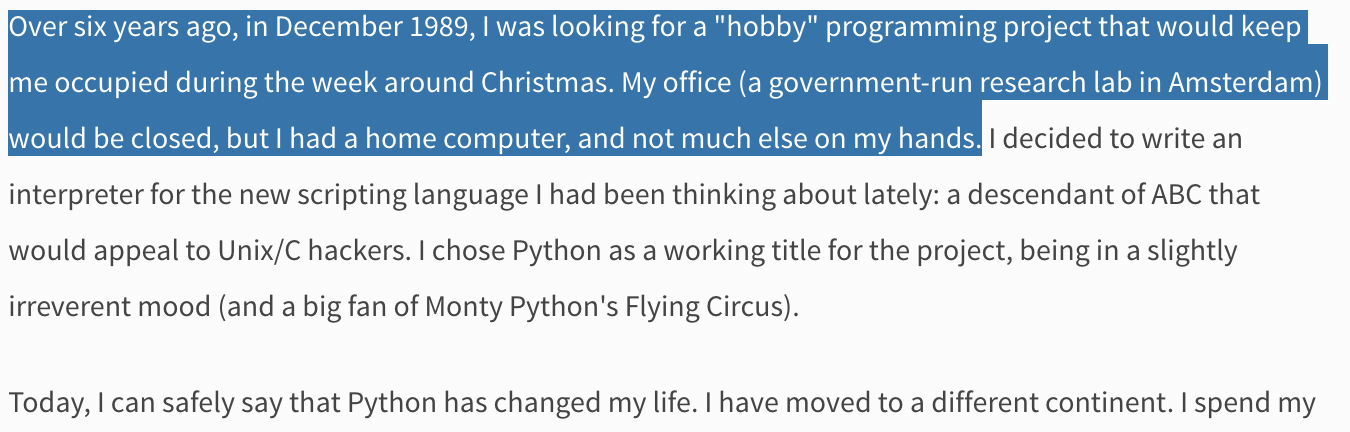
Python's history¶
The original project began in 1989.
- Release of Python 2.0 in 2000
- Release of Python 3.0 in 2008
We're using Python 3.0 in this class. Any number after the decimal is probably fine, though 3.6 or better is preferred for certain operations later on.
Wondering why a 2.x branch has survived almost two decades after its initial release?
Python 3 was designed as backwards-incompatible; a good number of syntax changes and other internal improvements made the majority of code written for Python 2 unusable in Python 3.
This made it difficult for power users and developers to upgrade, particularly when they relied on so many third-party libraries for much of the heavy-lifting in Python.
Until these third-party libraries were themselves converted to Python 3 (really only in the past couple years!), most developers stuck with Python 2.
Python, the Language¶
Python is an intepreted language.
Contrast with compiled languages like C, C++, and Java.
In practice, the distinction between interpreted and compiled has become blurry, particularly in the past decade.
- Interpreted languages in general are easier to use but run more slowly and consume more resources (JavaScript, Python, Matlab, and Ruby are examples of interpreted languages)
- Compiled languages in general have a higher learning curve for programming, but run much more efficiently (C, C++, Fortran, and Go are examples of compiled languages)
As a consequence of these advantages and disadvantages, modern programming languages have attempted to combine the best of both worlds:
- Java is initially compiled into bytecode, which is then run through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) which acts as an interpreter. In this sense, it is both a compiled language and an interpreted language.
- Python runs on a reference implementation, CPython, in which chunks of Python code are compiled into intermediate representations and executed.
- Julia, a relative newcomer in programming languages designed for scientific computing and data science, straddles a middle ground in a different way: using a "just-in-time" (JIT) compilation scheme, whereby code is compiled as the program runs, theoretically providing the performance of compiled programs with the ease of use of interpreted programs. JIT compilers have proliferated for other languages as well, including Python (but these are well beyond the scope of this course; take CSCI 4360 if interested!)
Python is a very general language.
It wasn't designed as a specialized language for performing a specific task. Instead, it relies on third-party developers to provide these extras.
As Python guru Jake VanderPlas put it:
"Python syntax is the glue that holds your data science code together. As many scientists and statisticians have found, Python excels in that role because it is powerful, intuitive, quick to write, fun to use, and above all extremely useful in day-to-day data science tasks."
Zen of Python¶
One of the biggest reasons for Python's popularity is its overall simplicity and ease of use.
Python was designed explicitly with this in mind!
It's so central to the Python ethos, in fact, that it's baked into every Python installation. Tim Peters wrote a "poem" of sorts, The Zen of Python, that anyone with Python installed can read.
To see it, just type one line of Python code (yes, this is live Python code--the text inside the gray box is the code, and the text underneath it is the output of the code):
import this
The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters Beautiful is better than ugly. Explicit is better than implicit. Simple is better than complex. Complex is better than complicated. Flat is better than nested. Sparse is better than dense. Readability counts. Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules. Although practicality beats purity. Errors should never pass silently. Unless explicitly silenced. In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess. There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it. Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch. Now is better than never. Although never is often better than *right* now. If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea. If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea. Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
These two lines are particular favorites of mine:
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.Line 1:
- Code that's hard to read or explain to anyone else is always a bad idea, no matter how well it runs.
- If you wrote it, fix it. If you didn't write it, find who did and have them fix it.
Line 2:
- "Easy to explain" is a requirement, but it doesn't necessarily mean the code is also good.
Don't you just feel so zen right now?
Part 2: Hello, World!¶
Enough reading, time for some coding, amirite?
print("Hello, world!")
Hello, world!
Yep! That's all there is to it.
Remember--text in a gray box is the actual Python code, while the text directly underneath it is the output (result) of that code.
Just for the sake of being thorough, though, let's go through this command in painstaking detail.
Functions: print() is a function.
- Functions take input, perform an operation on it, and give back (return) output.
You can think of it as a direct analog of the mathematical term, $f(x) = y$. In this case, $f()$ is the function; $x$ is the input, and $y$ is the output.
Later in the course, we'll see how to create our own functions, but for now we'll make use of the ones Python provides us by default.
Arguments: the input to the function.
- Interchangeable with "parameters".
In this case, there is only one argument to print(): the text that we want printed out. This text, in Python parlance, is called a "string". I can only presume it is so named because it is a string of individual characters.
We can very easily change the argument we pass to print():
print("This is not the same argument as before.")
This is not the same argument as before.
We could also print out an empty string, or even no string at all.
print("") # this is an empty string
print() # this is just nothing
In both cases, the output looks pretty much the same...because it is: just a blank line.
- After
print()finishes printing your input, it prints one final character--a newline.
This is basically the programmatic equivalent of hitting Enter at the end of a line, moving the cursor down to the start of the next line.
What are "strings"?¶
Strings are a type of data format (remember data formats from Greater Data Science?) in Python that exclusively uses alphanumeric (A through Z, 0 through 9) characters.
Look for the double-quotes!
"5" # This is a string.
5 # This is NOT a string.
5
What are the hashtags? (#)¶
The pound signs # are delineators for comments.
- Comments are lines in your program that Python ignores entirely.
- When you type a
#in Python, everything after that symbol on the same line is ignored.
Comments exist purely for coders to explain and clarify parts of the code directly in the code itself. It's kind of like making notes on the margins of a textbook.
I strongly encourage everyone to make liberal use of comments, even just to remind yourself what you were thinking! I can't count the number of times I worked on code, set it aside for a month, then came back to it and had absolutely no idea what I was doing.
Part 3: Beyond "Hello, World!"¶
Ok, so Python can print strings. That's cool. Can it do anything that's actually useful?
Python has a lot of built-in objects and data structures that are very useful for more advanced operations--and we'll get to them soon enough!--but for now, you can use Python to perform basic arithmetic operations.
Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division--they're all there. You can use it as a glorified calculator:
3 + 4
7
3 - 4
-1
3 * 4
12
3 / 4
0.75
Python knows how order of operations works, too:
3 + 4 * 6 / 2 - 5
10.0
(3 + 4) * 6 / (2 - 5)
-14.0
Take a moment to convince yourself.
Python even has a really cool exponent operator, denoted by using two stars right next to each other:
2 ** 3 # 2 raised to the 3rd power
8
3 ** 2 # 3 squared
9
25 ** (1 / 2) # Square root of 25
5.0
Now for something really neat:
y = 2
y * 3
6
This is an example of using Python variables.
- Variables store and maintain values that can be updated and manipulated as the program runs.
- You can name a variable whatever you like, as long as it doesn't start with a number ("
5var" would be illegal, but "var5" would be fine) or conflict with reserved Python words (likeprint).
Here's an operation that involves two variables:
x = 2
y = 3
x * y
6
We can assign the result of operations with variables to other variables:
x = 2
y = 3
z = x * y
print(z)
6
The use of the equals sign = is literally called the assignment operator (NOT the "equal" sign!).
- "Assignment" takes whatever value is being computed on the right-hand side of the equation and assigns it to the variable on the left-hand side.
- Multiplication (
*), Division (/), Addition (+), and Subtraction (-) are also operators.
Operators operate on things. Multiplication, division, addition, subtraction, assignment, and exponentiation are all operators.
What happens if I perform an assignment on something that can't be assigned a different value...such as, say, a number?
x = 2
y = 3
5 = x * y
File "<ipython-input-22-8ec6fd890370>", line 1 5 = x * y ^ SyntaxError: can't assign to literal
CRASH!
Ok, not really; Python technically did what it was supposed to do. It threw an error, alerting you that something in your program didn't work for some reason. In this case, the error message is can't assign to literal.
Let's parse out that error message, starting with the SyntaxError: prefix:
Erroris an obvious hint.
Syntaxgives us some context.
We did something wrong that involves Python's syntax, or the structure of its language. Specifically, we tried to assign (remember the assignment operator!) a value to a literal.
What's a literal? The "literal" being referred to is the number 5 in the operation: 5 = x * y
- We are attempting to assign the result of the computation of
x * yto the number 5
- However, 5 is known internally to Python as a "literal"
- 5 is literally 5; you can't change the value of 5! (5 = 8? NOPE)
So we can't assign values to numbers. What about assigning values to a variable that's used in the very same calculation?
x = 2
y = 3
x = x * y # zomg!
print(x)
6
This works just fine! In fact, it's more than fine--this is such a standard operation, it has its own operator:
x = 2
y = 3
x *= y # does exactly the same thing as before
print(x)
6
Out loud, it's pretty much what it sounds like: "x times equals y".
This is an example of a shorthand operator. You could absolutely live without it! It's purely there to make your life easier.
- We multiplied
xbyyand stored the product inx, effectively updating it.
- There are many instances where you'll want to increment a variable: for example, when counting how many of some "thing" you have.
- All the other operators have the same shorthand-update versions:
+=for addition,-=for subtraction, and/=for division.
You don't have to use these operators if they're confusing! They exist for your convenience, but if you'd rather write out x = x + 1 every time you increment a variable by 1, that's absolutely 100% OK.
Review Questions¶
1: Let's say you want to count the number of words in Wikipedia. You have a variable to track this count: word_count = 0. For every word you come across, you'll update this counter by 1. Using the shorthand you saw before, what would the command be to update the variable at each word?
2: What would happen if I ran this command? Explain. ("5" + 5)
3: What would happen if I ran these commands? Explain.
x = "5"
y = "10"
z = x + y
print(z)4: What would happen if I ran this command? Explain. x = y
Course Administrivia¶
- Please check that you're set up on Slack and JupyterHub! If you're having any problems accessing either of these, let me know ASAP.
- Please check out the revamped course website if you have questions; it should have pretty much all the information you need about the course!
- Assignment 0 comes out tomorrow! It doesn't have a deadline, but is instead an introduction to using JupyterHub. Please go through it, as we'll be using JupyterHub all semester for both homeworks AND exams!
Additional Resources¶
- Guido's PyCon 2016 talk on the future of Python: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgtL4S7Hrwo
- VanderPlas, Jake. Python Data Science Handbook. 2016 (pre-release).